The online retail landscape is undergoing a seismic shift, moving decisively beyond the familiar territory of search bars and sprawling marketplaces towards the dynamic realm of conversational interfaces. Artificial intelligence, once a background technology, is now stepping into the spotlight, fundamentally reshaping how consumers discover, research, and purchase products.
At the vanguard of this transformation stands ChatGPT, OpenAI’s sophisticated language model. No longer just a tool for answering questions or drafting text, ChatGPT, particularly powered by its latest iteration, GPT-4o, has evolved into a potent and increasingly indispensable shopping assistant. This evolution signifies more than an incremental upgrade; it heralds the dawn of a new era in e-commerce – conversational commerce – presenting both unprecedented opportunities and critical challenges for brands navigating the digital future.
This analysis delves into the intricacies of ChatGPT’s shopping capabilities, assesses its disruptive potential within the competitive e-commerce ecosystem, explores the profound implications for digital marketing strategies, provides actionable guidance for brands seeking to adapt, and projects the trajectory of AI-driven shopping in the coming years.
Dissecting ChatGPT’s Shopping Engine: Features and Functionality
The emergence of ChatGPT as a shopping tool is underpinned by significant advancements in its core technology and the introduction of specific, commerce-focused features. Understanding these components is crucial for appreciating their capabilities and potential impact.
Powered by GPT-4o: The Engine Driving the Experience
The foundation of ChatGPT’s enhanced shopping features is GPT-4o, OpenAI’s flagship model introduced in May 2024. Billed as providing GPT-4 level intelligence with significantly improved speed and capabilities across text, voice, and vision, GPT-4o represents a leap forward in multimodal AI. The “o” signifies “omni,” reflecting its ability to natively process and generate combinations of text, audio, image, and eventually video inputs. While the current shopping features primarily leverage text and image understanding, the underlying omnimodal architecture allows for richer interpretation of queries and visual product information.1
GPT-4o boasts enhanced quality and speed in over 50 languages, making the shopping features more accessible globally.1 Crucially, OpenAI began rolling out GPT-4o and its associated features, including advanced data analysis and web browsing (which powers the shopping results), to both paid (Plus, Team, Enterprise) and free users, albeit with message limits for the free tier.1 This broad accessibility, available even to logged-out users, is a key strategic element accelerating the adoption of ChatGPT as a shopping tool. Further refinements to GPT-4o have focused on improving instruction following, problem-solving, and conversational flow, making interactions feel more intuitive and collaborative.
From Chat to Cart: Understanding the Core Features
ChatGPT integrates several key functionalities to create its shopping experience:
- Web Search Integration: The shopping capabilities are explicitly tied to ChatGPT’s ability to browse the web in real-time.1 When a user’s query indicates shopping intent (e.g., “best espresso machines under $200”), ChatGPT utilises its search function to gather relevant, up-to-date product information.
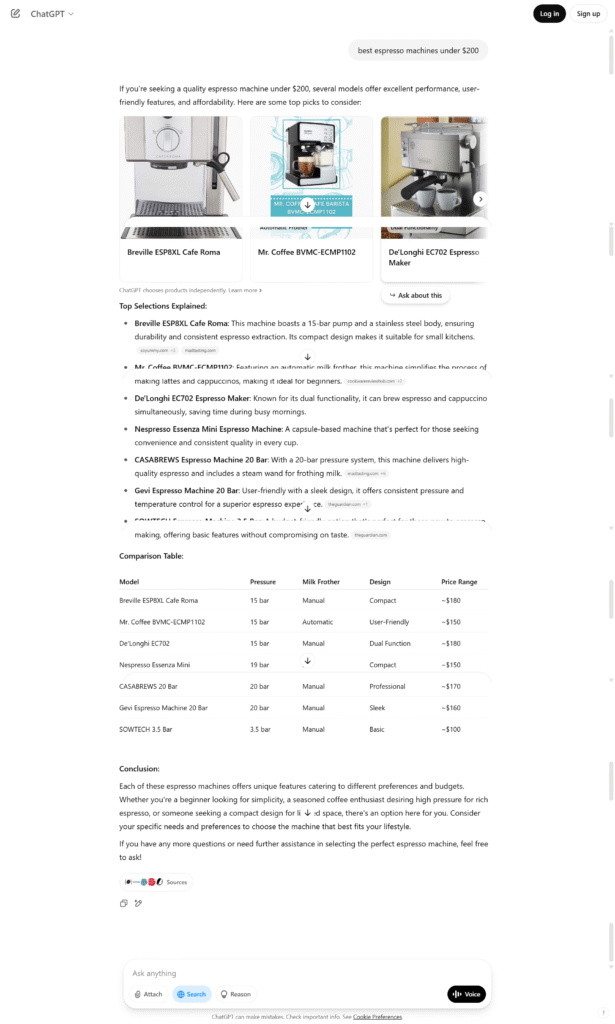
- Product Cards: Instead of just text links, ChatGPT presents product recommendations in visually appealing cards directly within the chat interface. These cards typically feature a product image, current price, an aggregated customer star rating, and a concise summary of key features. The layout often resembles familiar interfaces like Google Shopping, providing a degree of user familiarity.
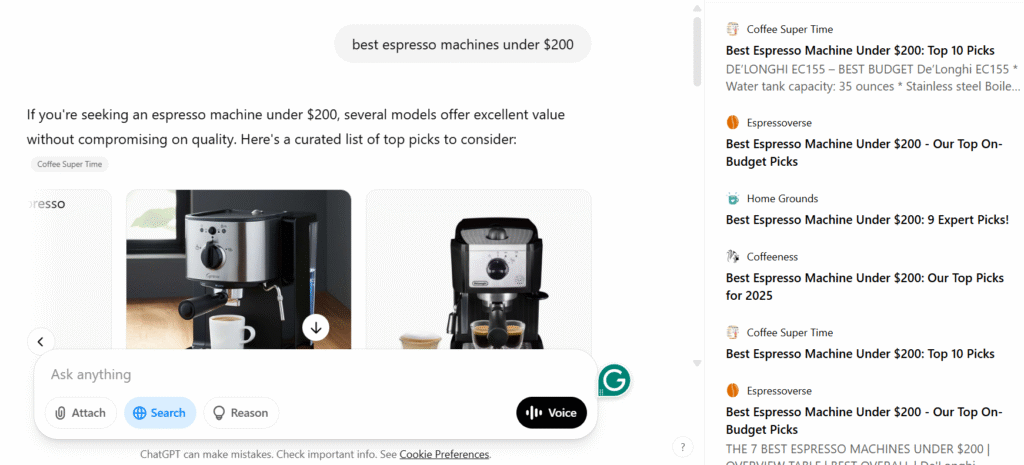
- Detailed Sidebar: Clicking on a product card activates a sidebar offering more comprehensive information. This sidebar functions as a comparison hub, listing multiple retailers (such as Amazon and Best Buy) that stock the item, alongside their real-time pricing. It often aggregates user reviews from various sources, including retailer sites and forums like Reddit, providing a holistic view of customer sentiment. Direct “Buy” buttons are prominently displayed next to each retailer listing.
- “Ask about this” Button: To facilitate deeper exploration without disrupting the flow, product cards may include an “Ask about this” button. This allows users to pose follow-up questions specifically about that product directly within the current context.
- Checkout Process: It is important to note that ChatGPT acts as a discovery and comparison engine, not a final point of sale. When a user clicks a “Buy” button, they are redirected to the respective merchant’s website to complete the transaction. ChatGPT guides the initial stages but hands off the final checkout process.
The Conversational Edge: User Experience & Personalisation
What truly distinguishes ChatGPT’s shopping experience is its conversational nature and personalisation capabilities:
- Natural Language Queries: Users are not restricted to rigid keyword searches. They can ask detailed, nuanced questions in natural language, such as “What are the best travel backpacks under $100 that are carry-on compliant and have a separate laptop compartment?”. The AI is designed to understand this complexity and provide tailored results.
- Memory Integration: For paid users (Plus, Pro, Team, Enterprise) in eligible regions (excluding the EU, UK, and certain other European countries due to regulatory considerations), ChatGPT integrates its “Memory” feature. This allows the AI to remember user preferences stated explicitly (“Remember I only buy Brand X black t-shirts”) or inferred from chat history across sessions. This retained context enables highly personalized recommendations that align with individual tastes and past behavior. The AI determines relevance based on the query, general factors (price, ratings), user-provided criteria, and these remembered preferences.
- User Control over Memory: Recognising potential privacy implications, OpenAI provides users with granular control over the Memory feature. Users can enable or disable it entirely, view and delete specific stored memories, instruct the AI to forget information conversationally, or use a “Temporary Chat” mode for conversations they don’t want remembered or used for future personalisation.
This combination of natural language understanding and persistent memory allows ChatGPT to function less like a search engine and more like a knowledgeable personal shopping assistant, adapting its suggestions over time.
An Ad-Free Oasis? OpenAI’s Organic Approach
A cornerstone of ChatGPT’s current shopping proposition is its explicit commitment to organic, unbiased results:
- No Paid Placements: OpenAI has repeatedly stated that the product results shown are chosen independently based on relevance and are not advertisements or sponsored placements. This stands in stark contrast to platforms like Google Shopping, where paid ads heavily influence visibility and ranking.
- Data Sources: Recommendations are generated based on structured product metadata (pricing, descriptions) sourced from third-party providers and other publicly available web content, including customer reviews scraped from retailer sites, publisher reviews, and forums.4 ChatGPT may also generate simplified titles or descriptions for clarity. Labels like “Budget-friendly” are AI-generated based on available data, not verified guarantees.
- Merchant Selection: Currently, the list of merchants displayed in the sidebar is primarily determined by data from third-party providers, and OpenAI does not re-rank them based on factors like lowest price or shipping policies. However, OpenAI is exploring ways for merchants to provide product feeds directly, which could influence future selection processes.
- No Affiliate Kickbacks (Currently): OpenAI asserts that it does not currently receive commissions or kickbacks for purchases originating from ChatGPT links. However, the company acknowledges it is experimenting with monetization models, including potential affiliate partnerships in the future.
- UTM Tracking: Despite the lack of direct monetization, ChatGPT automatically appends the UTM parameter utm_source=chatgpt.com to the ‘Buy’ links. This allows merchants using web analytics platforms like Google Analytics 4 to accurately track referral traffic and attribute sales originating from ChatGPT, providing valuable data on its effectiveness as a channel.
This “organic-first” approach, combined with conversational interaction and personalisation, forms the core of ChatGPT’s unique value proposition in the crowded e-commerce search space. The seamless discovery funnel—moving from a natural language query to visual product cards, detailed comparisons, and direct buy links—offers a potentially smoother path than traditional keyword searching, especially for users unsure of exactly what they need or those undertaking complex purchase research.
However, the current reliance on third-party data introduces potential inaccuracies if those sources are flawed or incomplete , a challenge OpenAI seems poised to address by exploring direct merchant data feeds. Furthermore, the powerful Memory feature, while enhancing personalisation, walks a fine line with user privacy, necessitating robust controls and transparency.
Market Tremors: AI Adoption and Competitive Shifts
ChatGPT’s foray into shopping arrives amidst a broader surge in consumer adoption of generative AI tools for commerce, signaling a significant shift in market dynamics and intensifying competition among major technology players.
The Data Speaks: Consumers Embrace AI Shopping Assistants
Recent market data paints a clear picture of rapidly growing consumer interest in using AI for shopping tasks:
- Surging Traffic: Adobe Analytics reported an astonishing 1,300% year-over-year increase in referral traffic to U.S. retail websites from generative AI sources during the 2024 holiday season (November 1 – December 31), with a peak of 1,950% on Cyber Monday. This trend continued into early 2025, with February showing a 1,200% increase compared to just seven months prior (July 2024). While the overall volume of AI-referred traffic remains modest compared to established channels like paid search or email, its growth rate has been remarkable, doubling approximately every two months since September 2024.
- High Adoption & Intent: Surveys confirm this behavioral shift. Adobe found that 39% of U.S. consumers had already used generative AI for online shopping by early 2025, with a majority (53%) planning to do so within the year. Capgemini research similarly found high consumer interest, with 70% keen on AI integration in purchasing experiences and 46% enthusiastic about its impact. Top use cases identified by Adobe include conducting research (55% of AI users), receiving product recommendations (47%), seeking deals (43%), getting gift ideas (35%), finding unique products (35%), and creating shopping lists (33%). Similar explosive growth in AI-driven traffic was observed in the travel (1,700% increase) and financial services (1,200% increase) sectors between July 2024 and February 2025.
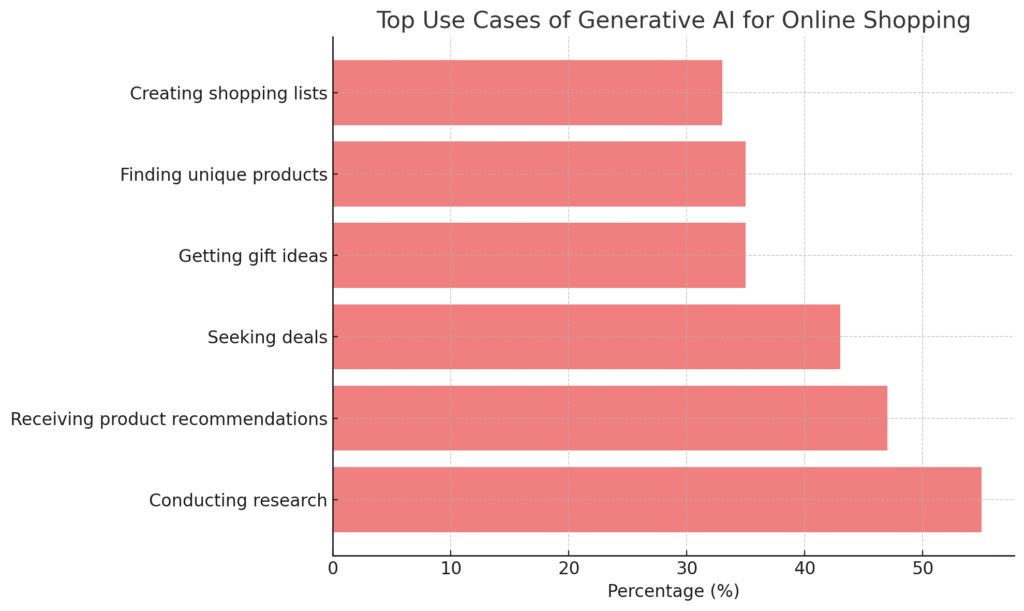
Other statistics corroborate this trend, with significant portions of consumers expressing interest in or already using chatbots for product information and customer support.
- Engagement & Satisfaction: Critically, traffic originating from generative AI sources demonstrates higher engagement. These visitors spend, on average, 8% more time on retail sites, browse 12% more pages per visit, and exhibit a 23% lower bounce rate compared to traffic from other sources.26 This suggests that the conversational nature of AI interactions helps users become more informed and confident. Satisfaction levels are also high: 92% of consumers who used AI for shopping found it enhanced their experience, and 87% stated they are more likely to use AI for larger or more complex purchases. Other studies report similar findings, with high percentages of users anticipating improved experiences with AI/bots and finding AI helpful.
- Conversion Gap & Usage Patterns: While highly engaged, AI-referred traffic initially showed a lower propensity to purchase directly. As of February 2025, this traffic was 9% less likely to convert compared to other sources. However, this represents a dramatic improvement from July 2024, when the conversion gap was 43%. This narrowing gap indicates that while AI is heavily utilised during the research and consideration phases, consumers are increasingly comfortable completing transactions following an AI interaction. Usage patterns also show a strong preference for desktop devices (86% share) for these conversational shopping experiences, likely due to the ease of interaction compared to mobile.
This data collectively validates the market opportunity OpenAI is targeting. Consumers are not only open to but actively embracing AI as a shopping tool, finding it enhances research, discovery, and overall engagement, paving the way for platforms like ChatGPT to gain significant traction.
Clash of the Titans: ChatGPT vs. Google vs. Amazon vs. Microsoft
ChatGPT’s entry into the shopping arena places it in direct competition with established tech giants, each leveraging their unique strengths and ecosystems:Google (Search / AI Overviews / SGE): As the dominant force in traditional search, Google is the most direct competitor and the incumbent ChatGPT seeks to disrupt. Google’s response is its Search Generative Experience (SGE), now often referred to as AI Overviews, which integrates AI-generated summaries and conversational capabilities directly into the search results page. This blends AI with traditional search listings and leverages Google’s vast index, advertising infrastructure, and ecosystem (Maps, Shopping, Local Service Ads).
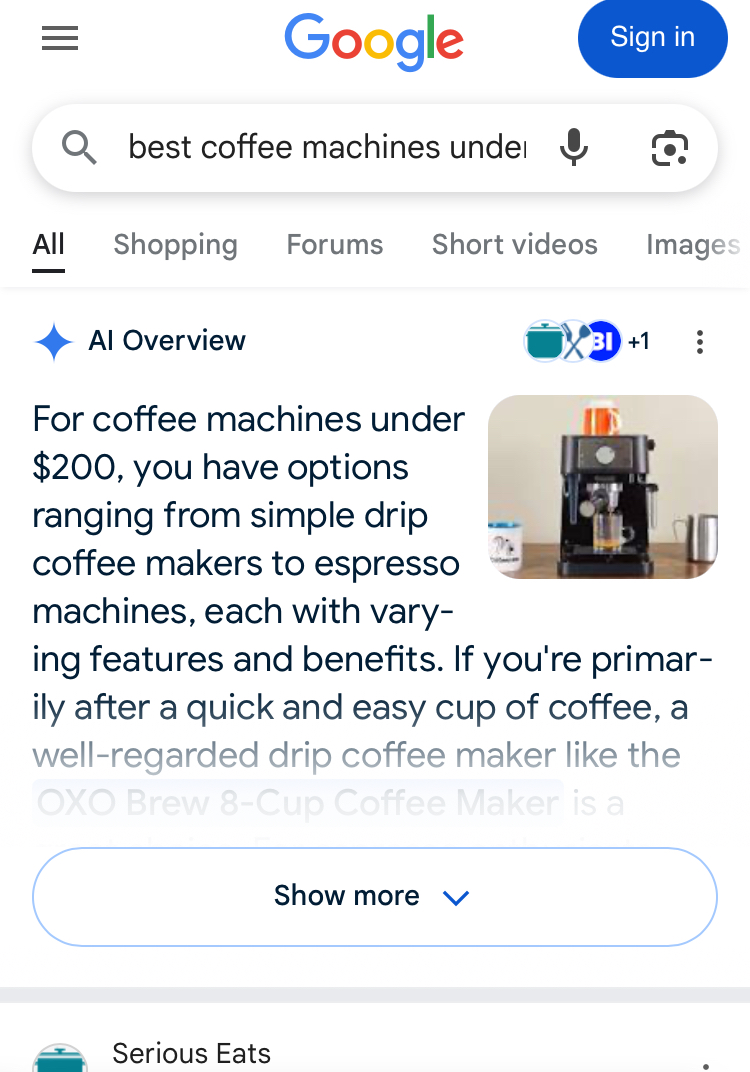
Key differences lie in the interface (ChatGPT’s pure chat vs. Google’s integrated search results) and the business model (ChatGPT’s current ad-free stance vs. Google’s heavily ad-influenced results). While SGE aims to provide quick answers, some perceive it as less conversational than ChatGPT and primarily focused on keeping users within Google’s ecosystem. User frustration with the declining quality of traditional Google search results, partly due to ads and potentially low-quality AI content, may create an opening for alternatives like ChatGPT.
- Amazon (Rufus): Amazon’s AI shopping assistant, Rufus, represents a different competitive angle – an AI deeply embedded within a massive existing e-commerce marketplace. Launched widely in the US in mid-2024, Rufus is trained specifically on Amazon’s extensive product catalog, millions of customer reviews, community Q&A, and web data. It offers conversational product discovery, comparisons, and recommendations directly within the Amazon app, integrated into both the search bar and product detail pages (PDPs). While functionally similar to ChatGPT in its conversational approach, Rufus’s strength lies in its unparalleled access to Amazon’s first-party retail data and transaction environment. Its potential weakness compared to ChatGPT might be a narrower scope of information beyond Amazon’s ecosystem and occasional reported inaccuracies or odd recommendations during its beta phase.
- Microsoft (Copilot / Bing): Microsoft’s Copilot is positioned as an AI companion integrated across its vast ecosystem, including Windows, the Edge browser, Bing search, and Microsoft 365 productivity suite. Copilot’s shopping capabilities allow it to research products, build comparisons, offer advice, alert users to price drops, and potentially facilitate purchases directly within the Copilot app or interface. It leverages Bing search data and, like ChatGPT, incorporates a Memory feature for personalisation. Copilot also features “Actions,” enabling it to perform tasks like booking travel or making reservations through partnerships with companies like Booking.com, Expedia, and OpenTable. Its competitive advantage lies in its deep integration with the operating system and productivity tools used by billions, particularly in enterprise environments.
This competitive dynamic suggests a fragmented future rather than a single winner-take-all scenario. Each platform leverages its core assets: OpenAI’s conversational AI prowess, Google’s search and advertising dominance, Amazon’s retail data and infrastructure, and Microsoft’s OS and enterprise footprint. Brands will likely need to develop strategies to ensure visibility and optimize experiences across multiple AI assistants, as consumers may interact with different ones depending on context (e.g., searching on Google, shopping on Amazon, working in Windows with Copilot, or having a dedicated chat with ChatGPT).
Table 1: Feature & Strategy Comparison: Leading AI Shopping Assistants
| Feature/Aspect | ChatGPT (OpenAI) | AI Overviews/SGE (Google) | Rufus (Amazon) | Copilot (Microsoft) |
| Underlying Model | GPT-4o / GPT-4.5 / Future Models | Gemini Models | Custom LLM (trained on Amazon data) | GPT-4o / Prometheus / Future Models |
| Primary Interface | Conversational Chat (Web, App) | Integrated into Google Search Results | Integrated into Amazon App (Search, PDPs) | Integrated (Windows, Edge, Bing, M365, App) |
| Product Discovery | Natural Language Queries | Keyword Search + AI Summary | Natural Language Queries within Amazon | Natural Language Queries / Contextual |
| Key Shopping Features | Product Cards, Sidebar Comparisons, Reviews, ‘Buy’ Links, “Ask about this” | AI Overviews, Product Attributes, Links to Retailers | Product Recommendations, Comparisons, Q&A on PDPs | Research, Comparisons, Advice, Price Alerts, Actions (e.g., booking) |
| Data Sources | Web Crawl (OAI-SearchBot), 3rd Party Metadata, Reviews (Web), User Memory | Google Index, Merchant Center Feeds, Knowledge Graph, Web | Amazon Catalog, Reviews, Q&A, Web Data | Bing Index, Web Data, User Memory, Partner Data (Actions) |
| Monetization (Current/Potential) | Subscription (Plus/Team/Ent), API Access. Potential: Affiliate Fees, Ads | Primarily Advertising (Search Ads, Shopping Ads) | Direct Product Sales, Marketplace Fees, Advertising [N/A – Implicit] | Subscription (Copilot Pro/M365), API Access. Potential: Transaction Fees (Actions) |
| Key Strength | Conversational Purity, Speed, Broad Web Knowledge | Search Dominance, Vast Index, Ecosystem Integration | Deep Integration with #1 E-commerce Platform, Rich 1P Data | OS/Productivity Suite Integration, Enterprise Reach |
| Key Weakness | Potential Monetization Pressure, Data Accuracy Reliance | Ad-Heavy Experience, User Frustration with Quality | Limited Scope Outside Amazon, Potential Bias | Less Consumer E-commerce Focus (Historically) |
| Privacy Approach (Memory/Data Use) | User Opt-in/Opt-out Memory, User Controls, Potential Training Use (unless opted out) | Integrated Google Account History/Activity Controls [N/A – Implicit] | Integrated Amazon Account History/Activity Controls [N/A – Implicit] | User Opt-in/Opt-out Memory, User Controls |
While ChatGPT’s current ad-free, organic approach is a significant differentiator, the immense operational costs and investor expectations surrounding AI development make future monetisation highly probable. Whether this takes the form of affiliate partnerships, “tasteful” advertising, or other models remains to be seen, but it could potentially dilute its unique value proposition over time compared to inherently commercial platforms like Google and Amazon.
The New E-commerce Playbook: Implications for Marketing and Brands
The ascent of AI shopping assistants like ChatGPT necessitates a fundamental rethinking of digital marketing strategies. Traditional playbooks that focused solely on optimising for keyword-based search engines are no longer sufficient. Brands must now adapt to a landscape where discovery happens through conversation, answers are valued over links, and structured data is paramount.
The Great Re-Optimisation: From SEO to Answer Engine Optimisation (AEO)
The most significant shift is the evolution from Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) to Answer Engine Optimisation (AEO). While SEO focuses on improving website ranking in traditional search results to earn clicks, AEO optimises content specifically to be understood, extracted, and presented directly by AI assistants and answer engines as the definitive answer to a user’s query. This is crucial because AI-generated summaries and direct answers (like Google’s Featured Snippets or AI Overviews, and ChatGPT’s responses) can lead to “zero-click” searches, where users get their information without visiting a brand’s website, potentially reducing organic traffic. AEO aims to ensure that a brand’s information is the answer the AI provides.
AEO is not a replacement for SEO but rather a complementary layer built upon strong SEO foundations. Key principles of AEO include:
- User Intent & Question Focus: The core of AEO is understanding the question behind the search, not just the keywords. Content must be framed to directly address specific user queries and anticipate follow-up questions. Utilising resources like Google’s “People Also Ask” section or tools like AnswerThePublic can help identify these questions
- Conversational Content: AI assistants operate conversationally, so content should be written using natural, clear, and accessible language. Formats like Q&A, comprehensive FAQ pages, and step-by-step “How-To” guides are highly effective as they mimic conversational flow and provide structured answers.
- Structured Content & Data: AI relies heavily on structure to parse information efficiently. Using clear headings (H1, H2, H3), short paragraphs, bullet points, numbered lists, and tables makes content easier for AI to digest and extract. Crucially, implementing Schema.org structured data markup is essential. This code explicitly tells search engines and AI the meaning and context of page elements (e.g., this text is an answer to a specific question, this is a product price, these are steps in a process).
- Conciseness (Snippet Bait): Answer engines often pull short summaries or snippets for direct answers (like Google’s Featured Snippets). Providing a concise, direct answer (often cited as 40-60 or 50-60 words) at the beginning of a relevant content section increases the likelihood of being featured.
- Authority & Trust (E-E-A-T): AI systems, like Google, prioritize information from credible sources. Demonstrating Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) is vital. This involves showcasing author credentials, citing reputable external sources, maintaining factual accuracy, securing positive reviews and mentions, and ensuring website security. Connecting to established entities in knowledge graphs (like Wikipedia or Wikidata) can also bolster authority.
- Content Freshness: Regularly updating content with current information, statistics, and examples signals relevance to AI engines.
- Technical Foundation: Solid technical SEO remains important. Ensuring the site is easily crawlable (especially by relevant bots like OAI-SearchBot), mobile-friendly, fast-loading, and secure (HTTPS) provides the necessary foundation for AEO.
Table 2: Essential Schema.org Types for AEO Success
Schema Type | Description/Use Case for AEO | Conceptual Implementation Notes |
FAQPage | Marks up Frequently Asked Questions sections. Helps AI extract direct question-answer pairs. | Wrap each Q&A pair within the mainEntity property using Question and AcceptedAnswer types. Ensure answers are concise. |
| QAPage | Similar to FAQPage, but typically for pages where a single question is answered, potentially by multiple users (e.g., forums). | Useful if your site hosts community Q&A. Helps AI identify the primary question and associated answers. |
| HowTo | Marks up step-by-step instructions for a task. | Define each step clearly using HowToStep. AI can extract these for sequential instructions or voice guidance. |
| Product | Provides detailed information about a product (name, image, description, brand, SKU, price, availability, reviews, rating). | Crucial for e-commerce. Allows AI to pull accurate product details for cards, comparisons, and price checks. |
Review / AggregateRating | Marks up individual reviews or an aggregated rating for a product, service, or business. | Helps AI understand customer sentiment and ratings, which are often incorporated into recommendations and summaries. |
LocalBusiness / Organization | Provides information about a business (name, address, phone, hours, logo, social links). | Essential for local AEO and brand entity recognition. Helps AI answer queries like “stores near me” or “brand contact info.” |
| Person | Identifies authors or key individuals, linking them to expertise and credentials. | Supports E-E-A-T signals by associating content with recognized experts. |
| Speakable | (Experimental/Limited Support) Identifies sections of content suitable for audio playback by voice assistants. | While adoption varies, it explicitly targets voice search AEO by highlighting concise, speakable answers. |
Implementing these schema types provides explicit signals to AI, making it significantly easier for them to understand and utilize content effectively for generating answers.
Monetising the Conversation: Affiliate Marketing and Beyond
While ChatGPT currently operates without direct affiliate commissions or paid placements , the economic realities of large-scale AI and stated future intentions suggest monetization is likely. OpenAI acknowledges experimenting with various models, potentially including affiliate fees. Financial projections reportedly include substantial revenue from “new products (including free user monetization)” starting as early as 2026.
This potential shift opens avenues for new affiliate marketing models tailored to AI platforms:
- AI-Mediated Affiliate Links: AI assistants could incorporate standard affiliate tracking codes into the ‘Buy’ links they provide, allowing platforms like OpenAI to earn commissions on resulting sales via redirects.
- Dedicated AI Partnerships: Brands or affiliate networks might establish direct partnerships with AI providers, perhaps by submitting affiliate-tagged product data feeds (aligning with OpenAI exploring direct feeds) or participating in specific partner programs. The discovery of Shopify-related code snippets in ChatGPT suggests such integrations are being actively developed.
- Content Licensing/Citation Fees: AI platforms might license high-quality review content from publishers or develop models where cited sources receive compensation, creating a new revenue stream for authoritative content creators.
For publishers and affiliate marketers, the immediate strategy involves focusing on AEO. Creating high-quality, trustworthy content that AI assistants are likely to cite becomes paramount. If ChatGPT frequently references specific review sites or blogs, securing placement on those platforms could become a primary driver of affiliate conversions. Marketers should also ensure their tracking mechanisms are robust enough to handle AI-driven referrals, potentially experimenting with ensuring UTM parameters or other identifiers persist through the AI interaction. Exploring existing AI-focused affiliate programs, like those offered by platforms such as CustomGPT.ai or Jasper AI, could also provide early insights.
Redefining Engagement: AI’s Impact on Customer Experience (CX)
AI assistants are poised to transform customer interactions, enabling deeper personalisation and more intuitive engagement:
- Hyper-Personalisation: Features like ChatGPT’s Memory allow AI to tailor recommendations and conversations based on a user’s entire interaction history, preferences, and explicitly stated needs. This moves beyond simple segmentation to truly individualised experiences, potentially increasing engagement and conversion rates. Adobe’s data showing higher engagement from AI referrals supports this potential.
- Conversational Interfaces: The shift is towards natural language interactions across the customer journey. This can manifest as AI-powered shopping assistants embedded on websites (like Amazon’s Rufus on PDPs), interactive chatbots providing support or recommendations, chat-based advertising formats, or voice-activated shopping experiences via smart speakers.
- Brand Implementations: Numerous brands are already leveraging AI, including ChatGPT technology, to enhance CX. Examples include:
- Sephora’s Virtual Artist: Uses AI for virtual makeup try-ons.
- Carrefour’s Hopla: A ChatGPT-based assistant offering product suggestions based on budget, diet, and menu ideas.
- Newegg: Uses ChatGPT for summarizing customer reviews (“Review Bytes”) and optimising other site content.
- Mercari’s Merchat AI: A ChatGPT-powered virtual shopping assistant guiding users to products.
- Duolingo Max: Uses GPT-4 for personalized language lessons and explanations.
- Snapchat’s My AI: Offers recommendations and creative assistance.
- Quizlet’s Q-Chat: An AI tutor built on the ChatGPT API.
- Other examples include using ChatGPT for generating product descriptions 100, social media content, email campaigns, customer service responses, personalised recommendations, and even vendor negotiations (Walmart).
These examples illustrate the versatility of AI in creating more efficient, personalised, and engaging customer experiences. However, the implementation requires careful consideration of brand voice consistency and ethical boundaries, particularly concerning the use of personal data gathered through features like Memory.
The move towards AEO signifies a crucial evolution, demanding content that is not just discoverable but authoritative, structured, and directly useful to AI. Similarly, the potential monetisation of AI assistants and their impact on CX require brands to rethink affiliate strategies and embrace conversational engagement, all while navigating the complexities of personalisation and privacy.
Strategic Imperatives: An Actionable Guide for Brands in the AI Era
Navigating the transition to AI-driven commerce requires proactive adaptation. Brands that strategically align their digital presence with how AI assistants discover and utilize information will gain a significant competitive advantage. The following provides a concrete action plan:
1. Optimize for AI Indexing & Discovery
Ensuring AI assistants can find and access relevant content is the foundational step.

- Configure robots.txt Correctly: Treat OpenAI’s search crawler, OAI-SearchBot, with the same importance as Googlebot. Review the website’s robots.txt file to explicitly allow OAI-SearchBot. Its user-agent string is Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko); compatible; OAI-SearchBot/1.0; +https://openai.com/searchbot. Importantly, allowing OAI-SearchBot enables content visibility in ChatGPT’s search features but does not opt the site into training OpenAI’s generative models – that is governed by a separate bot, GPTBot. Brands can choose to allow or disallow GPTBot independently based on their stance on AI training data. Also, consider allowing requests from OpenAI’s published IP ranges for these bots.
- Submit Product Data Feeds: OpenAI is exploring mechanisms for merchants to provide product information directly. Brands should proactively seek opportunities to submit structured product feeds. This ensures the AI has the most accurate, complete, and up-to-date information on inventory, pricing, specifications, and availability, bypassing potential scraping errors or delays.
- Leverage Bing Optimization: Given potential reliance or partnerships, optimizing for Bing’s web crawler and utilizing Bing Webmaster Tools to monitor indexing and diagnose issues can indirectly benefit visibility within ChatGPT Search.91
- Maintain Technical SEO Health: Fundamental technical SEO remains crucial. Ensure the website is easily crawlable with a logical site structure and effective internal linking. Prioritize fast page load speeds, implement a mobile-friendly responsive design, and secure the site with HTTPS.
2. Structure Data for AI Understanding
Making information machine-readable is critical for AI interpretation.
- Implement Robust Schema.org Markup: Go beyond basic schema. Implement comprehensive markup for all relevant entities, particularly Product (including nested properties like offers, aggregateRating, review), FAQPage, HowTo, QAPage, Organization, LocalBusiness, and Person schemas. Use tools like Google’s Rich Results Test to validate implementation.
- Ensure Consistent and Factual Product Information: Use precise and consistent product names, SKUs, and descriptions across the website and data feeds. Prioritize factual specifications and features, often presented in clear bullet points or tables, over purely marketing-driven language.
- Cultivate and Display User-Generated Content: Actively encourage and prominently display authentic customer reviews and Q&A sections on product pages. AI assistants frequently leverage this content to generate summaries, assess sentiment, and answer specific user questions.
3. Create Conversational & Authoritative Content
Content must be tailored to how users interact with AI and how AI evaluates information.
- Answer Specific Questions Directly: Develop content explicitly designed to answer the questions potential customers are asking. This includes dedicated FAQ pages, comprehensive “How-To” guides, “What is…” explainers, and incorporating Q&A formats within broader articles. Structure answers concisely, especially at the beginning of sections, to target featured snippets (“snippet bait”).
- Adopt Natural, Conversational Language: Write clearly and naturally, mirroring spoken language rather than relying on dense jargon or excessive keywords. Focus on being helpful and informative.
- Systematically Build E-E-A-T: Consciously build and showcase Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
- Expertise: Feature author bios with credentials, publish case studies, provide in-depth analysis.
- Authoritativeness: Cite reputable sources, earn high-quality backlinks and media mentions, secure positive press coverage.
- Trustworthiness: Gather positive customer testimonials and reviews, ensure website security (HTTPS), provide clear contact information, maintain factual accuracy, and ensure consistent branding across platforms. Ensure Knowledge Graph entities (Wikipedia, Wikidata) are accurate.
4. Embrace AI Tools & Experimentation
Leverage AI itself to enhance optimization efforts and explore new engagement models.
- Develop Custom GPTs or AI Assistants: Consider creating branded GPTs (using OpenAI’s platform) or custom AI chat assistants tailored to specific product lines or customer support functions. This allows for direct interaction and controlled recommendations.
- Utilize AI for Content Strategy and Creation: Employ AI tools (including ChatGPT) for tasks like identifying user intent, performing keyword research (especially for long-tail and conversational queries), generating topic ideas, drafting initial content outlines or descriptions, analyzing competitor content, and identifying content gaps.
5. Monitor, Analyze, and Adapt Continuously
The AI landscape evolves rapidly, requiring ongoing vigilance and adjustment.
- Track AI Referral Traffic: Implement robust analytics tracking. Specifically monitor traffic using the utm_source=chatgpt.com parameter in tools like Google Analytics 4 to understand volume and behavior. Analyze the Session Source dimension and conversion paths for this segment.
- Analyze Performance in AI: Regularly test relevant product and informational queries directly within ChatGPT (and other relevant AI assistants) to see if and how the brand’s products or content are being surfaced. Identify gaps where competitors are mentioned but the brand is not.
- Refine and Iterate: Use performance data and competitive analysis to continuously refine content strategies, structured data implementation, technical optimizations, and keyword targeting to improve visibility and relevance within the AI ecosystem.Track AEO-specific metrics like appearance in featured snippets or direct AI answers where possible.
Implementing these strategies requires a holistic approach, integrating efforts across technical SEO, content marketing, data management, and brand building. It represents a shift towards more direct engagement with AI platforms, moving beyond passive indexing to active optimization for AI understanding and citation. Success hinges on providing clear, structured, authoritative information in a format that AI can readily consume and trust. Continuous monitoring and adaptation will be crucial as AI models and algorithms inevitably evolve.
Gazing into the Crystal Ball: E-commerce from 2028-2030
Projecting the trajectory of AI’s influence on e-commerce over the next three to five years reveals a landscape potentially transformed, where conversational interfaces become central, optimization strategies mature, and consumer behaviors adapt to increasingly intelligent digital assistants.
AI as the Default Shopping Portal
By the 2028-2030 timeframe, it is highly probable that generative AI assistants like ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini/AI Overviews, Microsoft’s Copilot, Amazon’s Rufus, and emerging competitors will serve as the primary entry point for a substantial portion of online product discovery and comparison shopping journeys. The paradigm of typing keywords into a search bar will likely yield significant ground to more natural, conversational interactions. Consumers will increasingly turn to their smartphones, computers, smart speakers, and other connected devices to ask questions like, “Find me a durable, waterproof hiking boot under $150 with good ankle support,” or “What’s a thoughtful anniversary gift for a partner who loves sustainable fashion?”. AI assistants will be expected to provide instant, curated, and visually rich responses complete with product details, comparisons, and direct purchasing options.
Market forecasts support this vision of pervasive AI integration. The global conversational AI market is projected to surge, potentially reaching $61.69 billion by 2032.The generative AI software market alone is forecast to exceed $176 billion by 2030, representing a CAGR of nearly 50% from 2023.Forrester predicts a 36% annual growth rate for generative AI software through 2030, capturing 55% of the total AI software market by that year.
Crucially, the retail and e-commerce sector is expected to be a major beneficiary and driver of this growth, potentially accounting for 33% of the enterprise value created by generative AI by 2030.While overall global e-commerce continues its strong growth trajectory (Forrester projects $6.8 trillion by 2028), generative AI initiatives are expected to be a key contributing factor. The sheer scale projected suggests AI will move from a novel tool to a fundamental layer of the digital commerce infrastructure.
The AEO Endgame: Mature Optimization Strategies
As AI becomes a dominant channel, Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) will transition from an emerging discipline to a core competency for digital marketers. We can anticipate the maturation of AEO strategies and the ecosystem supporting them:
- Sophistication Beyond Basics: Optimization will move beyond simple structural markup and concise answers. Success will likely require deeper understanding of semantic relevance, entity recognition (connecting brands, products, features, and concepts), and knowledge graph optimization to ensure AI assistants grasp the full context and authority of a brand’s offerings.
- Specialized Tools and Services: A dedicated market for AEO tools and specialized agency services will likely emerge, offering capabilities for AI visibility tracking, competitive analysis within AI platforms, automated schema generation, and content optimization specifically for AI citation.
- Evolved Analytics: Measurement will adapt. Marketers will track new metrics focused on “AI visibility” – how often a brand is mentioned or cited in AI responses, the sentiment of those mentions, and the conversion rates from AI-driven referrals, moving beyond traditional SERP rankings and click-through rates.
The Business of AI Commerce: Revenue Models and Partnerships
The current ambiguity around monetization for platforms like ChatGPT will likely resolve as the market matures. Several models or combinations could emerge:
- Affiliate Fees Become Standard: It’s highly probable that AI assistants facilitating product discovery and purchase will incorporate affiliate links as a primary revenue stream, taking a commission on sales they initiate. This aligns with OpenAI’s acknowledged experimentation and revenue projections.
- “Tasteful” Advertising Models: While OpenAI’s CEO has expressed distaste for traditional disruptive ads, pressure for revenue might lead to sponsored product placements or subtle advertising formats integrated within conversational results, perhaps clearly labeled as such.20 The challenge will be balancing monetization with user trust and the promise of unbiased results.
- Direct Platform Partnerships: Deeper integrations, like the potential OpenAI-Shopify connection, could become more common. Brands might pay for premium placement, enhanced features within the AI interface, or access to anonymized user intent data.
- Content Licensing: AI platforms might pay publishers or creators for licenses to use their high-quality review content or data to train their models and generate more authoritative responses.
Brands will need to prepare for these models by ensuring their affiliate programs are AI-compatible, exploring potential direct partnerships, and continuing to produce high-value content that AI platforms might license or cite organically.
Marketing’s Metamorphosis: AI-Native Workflows
Digital marketing itself will undergo significant transformation, with AI becoming deeply embedded in operational workflows:
- AI-Driven Content & Personalization: AI will likely automate large parts of content creation (drafting product descriptions, blog posts, ad copy), personalized email campaigns, and dynamic website experiences, freeing marketers to focus on strategy and creativity.
- Conversational Marketing Dominance: Marketing communications will become increasingly conversational, leveraging chatbots and AI assistants for outreach, lead qualification, customer support, and even sales interactions. Traditional channels like email marketing might see reduced prominence compared to AI-driven chat engagement.
- Rise of AI Optimization Services: Agencies and internal teams will offer specialized services focused on optimizing websites and data for AI visibility (AEO), developing custom AI agents or GPTs, and managing AI-powered advertising campaigns.
- Integrated Commerce Experiences: The lines between social media, content consumption, and commerce will blur further, with AI facilitating seamless transitions from discovery (e.g., seeing a product on social media) to purchase (e.g., initiating a ChatGPT shopping session).
The Evolved Consumer: Expectations, Behavior, and Privacy Dynamics
Consumer behavior will adapt to the capabilities and prevalence of AI shopping assistants:
- Heightened Expectations: Users will expect instant, accurate, and highly personalized assistance as the norm. Tolerance for irrelevant results, clunky interfaces, or generic recommendations will decrease.
- More Informed Decisions: The ability of AI to quickly synthesize product information, compare options, and summarize reviews may lead to more deliberate and informed purchasing decisions, as suggested by current higher engagement rates for AI-referred traffic. Conversion rates for brands effectively leveraging AI channels could increase significantly.
- The Privacy Paradox Persists: The tension between personalization and privacy will remain a critical factor. While users value tailored experiences, concerns about data collection, security breaches , and potential manipulation will persist. Regulatory frameworks (like GDPR) and user demand for transparency and control will likely shape how AI platforms manage and utilize personal data. Brands that prioritize ethical data handling and transparency will likely build greater trust.
- Workforce Impacts: The increased automation driven by AI in retail and customer service could lead to significant shifts in job roles and required skills within the industry.
By 2028-2030, generative AI is expected to be inextricably woven into the fabric of online commerce. The platforms and strategies dominating this landscape will be those that master the art of providing relevant, trustworthy, and seamless assistance within a conversational context, while successfully navigating the evolving dynamics of monetization and user privacy. Brands ignoring this shift risk becoming increasingly marginalized in the primary discovery channels of the future.
Conclusion: Adapt or Be Disrupted – The Time to Act is Now
The digital commerce landscape is undergoing a transformation as profound and rapid as any seen before. Generative artificial intelligence, the technology that has already reshaped content creation and information retrieval, is now poised to fundamentally alter how consumers shop online. ChatGPT’s introduction of sophisticated shopping features, powered by GPT-4o and integrated web search, is not a distant hypothetical but a live, globally accessible reality.1 These capabilities, enabling natural language product queries, visual comparisons, personalized recommendations, and direct purchase links, signal the maturation of conversational commerce.
Over the coming years, the data strongly suggests that consumers will increasingly adopt AI assistants as their primary tools for product discovery, research, and comparison. The convenience, personalization, and efficiency offered by platforms like ChatGPT are resonating with users, driving significant engagement and satisfaction. This shift in behavior presents a clear and compelling mandate for brands and marketers.
The imperative is to adapt, and to do so quickly. The traditional SEO playbook, while still relevant, is insufficient in an era where visibility increasingly depends on being cited directly by an AI. Embracing Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) is no longer optional but essential. This requires a strategic focus on creating high-quality, authoritative content structured for AI understanding, implementing robust Schema.org markup, ensuring technical accessibility for AI crawlers like OAI-SearchBot, and cultivating trust signals (E-E-A-T).
Brands that proactively undertake this adaptation will position themselves to capture high-intent shoppers at the critical early stages of their journey within these emerging conversational channels. This translates directly into opportunities for more seamless customer acquisition, potentially higher conversion rates driven by informed engagement, and access to new revenue streams as AI platforms evolve their monetization models.
Conversely, inaction carries significant risk. Businesses that fail to optimize for AI discovery risk becoming invisible to a growing segment of consumers who start their shopping journeys not with a search bar, but with a conversation. The rapid pace of AI development and consumer adoption leaves little room for complacency.
Therefore, the time to act is unequivocally now. Businesses must audit their digital assets for AI readiness, refine their content strategies to align with conversational search patterns, and invest in the technical infrastructure (like structured data and potentially product feeds) needed to “speak the language” of AI. Viewing platforms like ChatGPT not as adversaries, but as powerful new conduits within the sales funnel is key to navigating this transition successfully. The future of e-commerce is conversational, and the brands that master this new dialogue will be the ones to thrive in the years ahead.
Sources
The insights and analysis presented in this report are informed by official announcements and documentation from OpenAI, including details on GPT-4o, ChatGPT search features, the OAI-SearchBot crawler, and the Memory function.
Findings are corroborated and expanded upon by reporting from reputable technology and business news outlets such as Reuters, TechCrunch, Wired, The Verge, Mashable, ZDNet, CNET, and others who covered the launch and functionality of ChatGPT’s shopping capabilities. Market data on AI adoption in e-commerce, consumer behavior, and engagement metrics primarily draws from extensive reports published by Adobe Analytics.
Competitive analysis incorporates information regarding Google’s AI Overviews/SGE, Amazon’s Rufus assistant, and Microsoft’s Copilot features, based on company announcements and industry reporting. Projections regarding market growth and future trends incorporate data and forecasts from analyst firms including Gartner, Forrester, and ABI Research, alongside other statistical sources like Statista and eMarketer. Best practices for Answer Engine Optimisation (AEO) synthesise recommendations from numerous digital marketing publications and expert analyses focused on optimising content for AI visibility.

